Trial Balance Example Format How to Prepare Template Definition
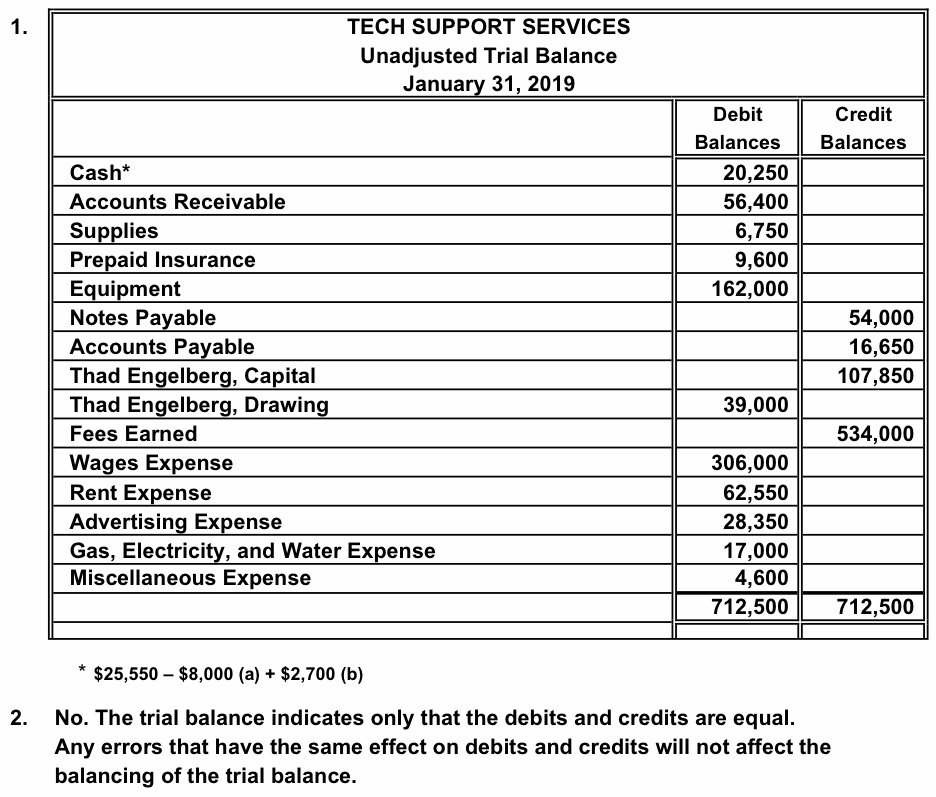
The main purpose of the unadjusted trial balance is to ensure that the total debits equal the total credits. It’s a preliminary step, and if there are discrepancies, it indicates there might be errors in the journal entries or ledger accounts. Following these adjustments, an “Adjusted Trial Balance” is prepared, which serves as the basis for preparing the financial statements of the entity.
FAR CPA Practice Questions: Journal Entries for Treasury Stock Transactions
This report provides a snapshot of the company’s accounts at a raw level, displaying the balances without considering necessary adjustments. An unadjusted trial balance is a list of all the company’s accounts and the balances in each account before any adjustments to the financial statements are made. An unadjusted trial balance is a listing of all the company’s accounts and their balances at a specific point in time, usually at the end of an accounting period before any adjusting entries have been made.
Step 2 of 3
It involves allocating the cost of tangible assets over their useful lives. For example, if a company purchases machinery, the expense is not recorded all at once but spread out over several years. This adjustment helps in matching the expense with the revenue generated from the asset, providing a clearer view of the company’s profitability. It acts as an initial diagnostic tool that signals whether further investigation is needed before proceeding with adjusting entries and eventual financial statement preparation.
Impact on Financial Statements
A trial balance is an important step in the accounting process, because it helps identify any computational errors throughout the first three steps in the cycle. Adjusting entries are a fundamental part of the accounting process, ensuring that financial statements reflect the true financial position of a business. One common adjustment involves accrued revenues, which are earnings that have been generated but not yet recorded in the books. For instance, a company may have provided services in December but will not invoice the client until January. To accurately reflect this revenue in the correct accounting period, an adjusting entry is made to recognize the income in December. The purpose of the trial balance is to test the equality between total debits and total credits after the posting process.
- Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise.
- For example, if a company purchases machinery, the expense is not recorded all at once but spread out over several years.
- Before computers, a ledger was the main tool for ensuring debits and credits were equal.
- This is simply a list of all the account balances straight out of the accounting system.
- However, most businesses can streamline this cycle and skip tedious steps like posting transactions to the general ledger and creating a trial balance.
Company
By recording these expenses in the period they were incurred, the company ensures that its financial statements present a more accurate picture of its liabilities and expenses. Creating an unadjusted trial balance is not just about finding errors though; it sets the stage for making important adjustments later on. These fine-tunings help present a true financial position before final reports are prepared. To embark on the preparation of an unadjusted trial balance, one must meticulously gather and synthesize data from the general ledger—a foundational step that sets the stage for accurate financial reporting. It catches every sale, purchase, payment, and receipt in the accounting records. The unadjusted trial balance takes center stage before year-end adjustments enter the picture.
It lays out raw financial data straight from the accounting records, serving as evidence of all monetary transactions up until that moment. Since the debit and credit columns equal each other totaling a zero balance, we can move in the year-end financial statement preparation process and finish the accounting cycle for the period. If it’s out of balance, something is wrong and the bookkeeper must go through each account to see what got posted or recorded incorrectly. Bookkeepers typically scan the year-end trial balance for posting errors to ensure that the proper accounts were debited and credited while posting journal entries.

This initial check-up is essential for an accurate balance sheet and income statement later on. Once all necessary corrections have been made and adjusted accounts reflect updated balances, this trial balance becomes known as an adjusted trial balance. Let’s now take a look at the T-accounts and unadjusted trial balance for Printing Plus to see how the information is transferred from the T-accounts to the unadjusted trial balance. The unadjusted trial balance (UTB) is an important tool for monitoring your company’s operating results. Create a master list of accounts (assets, liabilities, equity, revenue & expenses) used in your company’s accounting system.
After an should taxes on stock influence your decision to buy or sell has been adjusted with the year-end closing entries, it is considered an adjusted trial balance. The year-end adjusting journal entries include booking prepaid and accrual accounts, recording dividends issued, and the closing entries for the year of the year. These adjusted account balances are then used to create the year-end financial statements.

