Book Value per Share Formula How to Calculate BVPS?

BVPS relies on the historical costs of assets rather than their current market values. This approach can lead to significant discrepancies between the book value and the actual market value of a company’s assets. Book Value Per Share is calculated by dividing the total common equity by the number of outstanding shares. Although infrequent, many value investors will see a book value of equity per share below the market share price as a “buy” signal. But an important point to understand is that these investors view this simply as a sign that the company is potentially undervalued, not that the fundamentals of the company are necessarily strong. Another way to increase BVPS is for a company to repurchase common stock from shareholders.
Book value per share and tangible book value per share
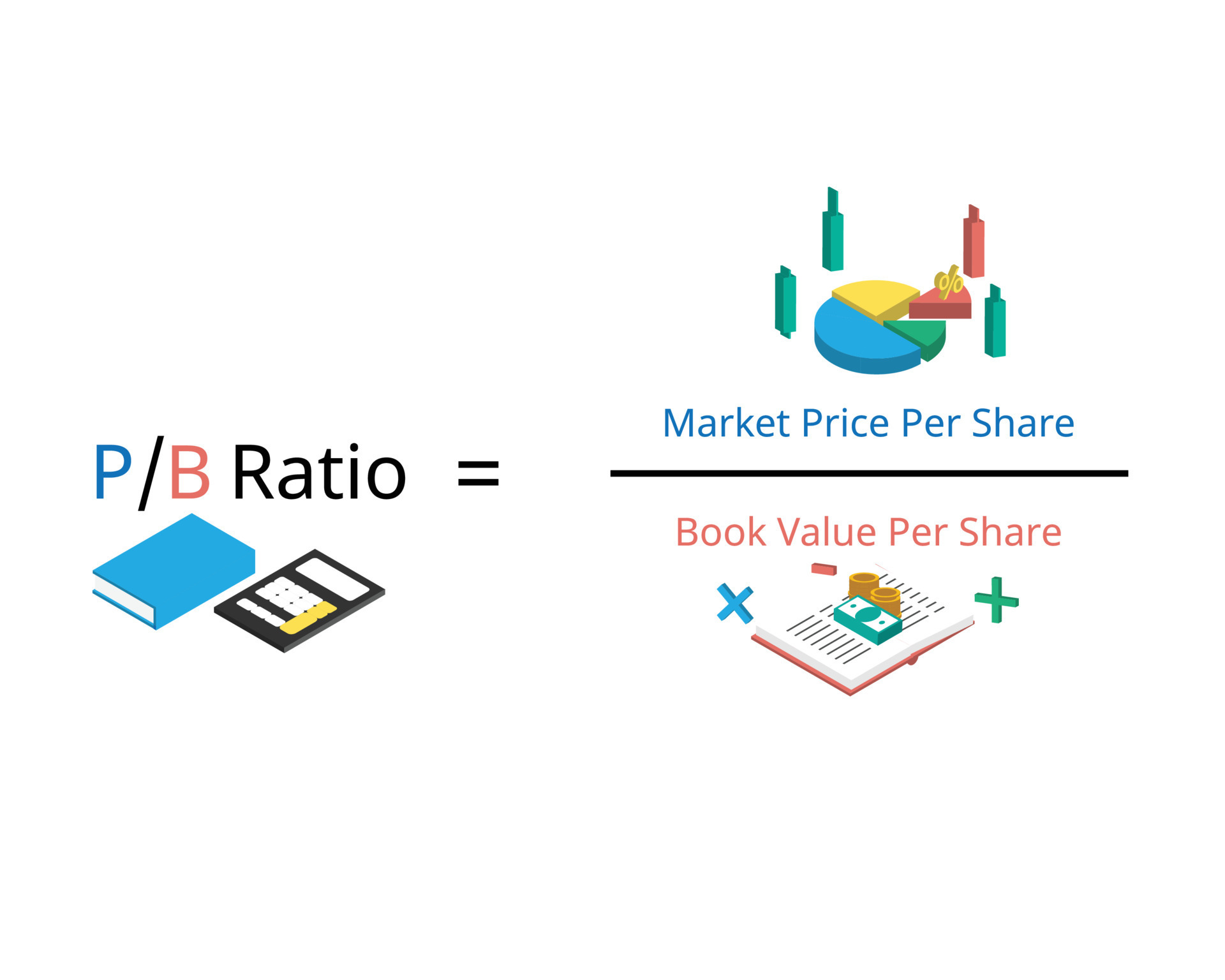
Conversely, if the market value per share exceeds BVPS, the stock might be perceived as overvalued. BVPS offers a baseline, especially valuable for value investors looking for opportunities in underpriced stocks. Even though book value per share isn’t perfect, it’s still a useful metric to keep in mind when you’re analyzing potential investments.
Limitations of BVPS
Book value per share (BVPS) tells investors the book value of a firm on a per-share basis. Investors use BVPS to gauge whether a stock price is undervalued by comparing it to the firm’s market value per share. Book value refers to a firm’s net asset value (NAV) or its total assets minus its total liabilities. The book value of a company is based on the amount of money that shareholders would get if liabilities were paid off and assets were liquidated. The market value of a company is based on the current stock market price and how many shares are outstanding. For example, let’s say that ABC Corporation has total equity of $1,000,000 and 1,000,000 shares outstanding.
Book Value per Share Calculator
This is why it’s so important to do a lot of research before making any investment decisions. There are a number of other factors that you need to take into account when considering an investment. For example, the company’s financial statements, competitive landscape, and management team. You also need to make sure that you have a clear understanding of the risks involved with any potential investment.
The Difference Between Market Value per Share and Book Value per Share
The Book Value Per Share (BVPS) is the per-share value of equity on an accrual accounting basis that belongs to the common shareholders of a company. A company can use a portion of its earnings to buy assets that would increase common equity along with BVPS. Or, it could use its earnings to reduce liabilities, which would also increase its common equity and BVPS. It is worth mentioning that the asset value recorded in the balance sheet is discounted by its depreciation period by period; thus, we should expect a decreasing equity value over time. That can happen; however, in successful companies, when the return on assets is high, constant, and stable, the depreciation effect is offset by the cash retained from the company. BVPS is significant for investors because it offers a snapshot of a company’s net asset value per share.
- If the market price for a share is higher than the BVPS, then the stock may be seen as overvalued.
- Conceptually, book value per share is similar to net worth, meaning it is assets minus debt, and may be looked at as though what would occur if operations were to cease.
- BVPS is crucial for investors as it helps determine whether a stock is overvalued or undervalued compared to its market price.
- Should the company dissolve, the book value per common share indicates the dollar value remaining for common shareholders after all assets are liquidated and all creditors are paid.
However, this should be considered alongside other factors like industry trends, company growth prospects, and overall market conditions. In the world of finance and investment, understanding balance sheet: definition example elements of a balance sheet a company’s true value is crucial for making informed decisions. While market price often dominates discussions, savvy investors know the importance of looking beyond surface-level metrics.
Book value per share (BVPS) is a fundamental financial metric that represents a company’s net asset value on a per-share basis. It’s calculated by dividing the company’s total equity (minus preferred equity) by the number of outstanding shares. BVPS is crucial for investors as it helps determine whether a stock is overvalued or undervalued compared to its market price. Book value is the value of a company’s total assets minus its total liabilities.
The ratio may not serve as a valid valuation basis when comparing companies from different sectors and industries because companies in other industries may record their assets differently. If the market price for a share is higher than the BVPS, then the stock may be seen as overvalued. There is also a book value used by accountants to value the assets owned by a company.

