How to Calculate Return on Common Stockholders Equity? An Accurate Guide
Analysts also consider ROE from a management standpoint, as it helps evaluate the team’s effectiveness in using investment capital to develop new products, streamline operations, or expand market share. Calculating this ratio helps investors understand the performance of their shares and assists in making informed comparisons between companies across industries. This metric indicates how well a company uses the capital from its common stockholders to generate net income. A high ROCE signifies superior utilization of common equity, but this figure should be interpreted against industry averages and historical performance.
Interpreting ROCE Values
Whether an ROE is deemed good or bad will depend on what is normal among a stock’s peers. For example, utilities have many assets and debt on the balance sheet compared to a relatively small amount of net income. A technology or retail firm with smaller balance sheet accounts relative to net income may have normal ROE levels of 18% or more. Like any other financial ratio, return on common equity should not be used in isolation. One approach is to decrease the total amount of shareholder equity, which can be achieved by buying back some of its own shares from investors. A strong ROE ratio varies by industry, but generally, an ROE above 15% to 20% is considered strong, indicating effective use of shareholders’ equity to generate profits.
Return on Equity Calculator (ROE) Excel Template
- A technology or retail firm with smaller balance sheet accounts relative to net income may have normal ROE levels of 18% or more.
- This ratio provides valuable insights into the potential profitability of funds invested in a company.
- ROE is closely related to measures like return on assets (ROA) and return on investment (ROI).
- Return on equity is a common financial metric that compares a company’s income to its total shareholders’ equity.
That’s because different types of companies have varying levels of assets and debts on their balance sheets and differing levels of income. A company with decent ROE tells you that buying its stock will likely be a lucrative investment over the long term. ROE is closely related to measures like return on assets (ROA) and return on investment (ROI). The equity of a company consists of paid-up ordinary share capital, reserves, and unappropriated profit. Still, as a rule of thumb, rates that exceed the average for the company’s industry can be considered strong.
Advantages of ROCE
Return on Common Equity (ROCE) is a crucial financial ratio that measures a company’s ability to generate profits from its invested capital. Investors and analysts often use ROCE as an indicator of a company’s financial performance and management efficiency. The return on equity ratio or ROE is a profitability ratio that measures the ability of a firm to generate profits from its shareholders investments in the company. In other words, the return on equity ratio shows how much profit each dollar of common stockholders’ equity generates. Return on common stockholders’ equity is calculated by dividing a company’s net income by its average common stockholders’ equity.
This could be due to better management, more favorable market conditions, or other factors. A positive ROE signifies that a company efficiently generates profits from its equity financing. For potential and current investors, ROE is a crucial factor to consider as it provides insight into a company’s efficiency at converting the investment into profit. definition of form 941 In today’s digital age, a slew of software and online platforms offer simplified, automated solutions for calculating financial metrics like ROCE. These tools can fetch necessary financial statements and compute the metric with minimal user input. Enhancing operational efficiency and keeping a tight rein on expenses will directly benefit net income.
Company
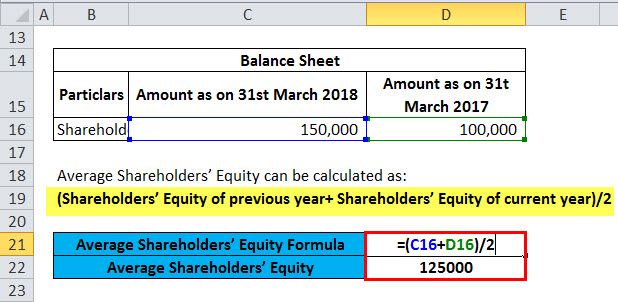
In general, both negative and extremely high ROE levels should be considered a warning sign worth investigating. An extremely high ROE can be a good thing if net income is extremely large compared to equity because a company’s performance is so strong. Average shareholders’ equity is calculated by adding equity at the beginning of the period. The beginning and end of the period should coincide with the period during which the net income is earned.
This is because common shareholders’ equity is not a fixed number and can change, for example, if a company sells additional stock. Apart from measuring a company’s current profitability, the return on common stockholders’ equity ratio can also be used to evaluate the historical financial performance of a business over a period of time. The return on common shareholders’ equity ratio is a financial metric that is used to measure a company’s ability to generate profits for equity investors.
Relatively high or low ROE ratios will vary significantly from one industry group or sector to another. Expressed in percentages, this is the rate of return that common stockholders get if they acquired stocks at par value, which is recorded in the balance sheet. Ultimately, when computing ROE, it is essential to consider the denominator and the income a company generates from the shareholder’s equity. The shareholder equity amount used in the formula is usually averaged for the period being evaluated. A company with a lower ROE but a solid balance sheet and steady growth potential may be a better investment than one with a higher ROE that has a high level of debt. It’s also essential to consider industry trends and market conditions to make informed investment decisions that align with your financial goals.

